This list of Linux Networking commands and scripts, will receive ongoing updates, similar to the other lists on this blog…
arpwatch – Ethernet Activity Monitor.
bmon – bandwidth monitor and rate estimator.
bwm-ng – live network bandwidth monitor.
curl – transferring data with URLs. (or try httpie)
darkstat – captures network traffic, usage statistics.
dhclient – Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Client
dig – query DNS servers for information.
dstat – replacement for vmstat, iostat, mpstat, netstat and ifstat.
ethtool – utility for controlling network drivers and hardware.
gated – gateway routing daemon.
host – DNS lookup utility.
hping – TCP/IP packet assembler/analyzer.
ibmonitor – shows bandwidth and total data transferred.
ifstat – report network interfaces bandwidth.
iftop – display bandwidth usage.
ip (PDF file) – a command with more features that ifconfig (net-tools).
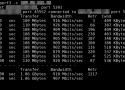
iperf3 – network bandwidth measurement tool. (above screenshot Stacklinux VPS)
iproute2 – collection of utilities for controlling TCP/IP.
iptables – take control of network traffic.
IPTraf – An IP Network Monitor.
iputils – set of small useful utilities for Linux networking.
iw – a new nl80211 based CLI configuration utility for wireless devices.
jwhois (whois) – client for the whois service.
“lsof -i” – reveal information about your network sockets.
mtr – network diagnostic tool.
net-tools – utilities include: arp, hostname, ifconfig, netstat, rarp, route, plipconfig, slattach, mii-tool, iptunnel and ipmaddr.
ncat – improved re-implementation of the venerable netcat.
netcat – networking utility for reading/writing network connections.
nethogs – a small ‘net top’ tool.
Netperf – Network bandwidth Testing.
netsniff-ng – Swiss army knife for daily Linux network plumbing.
netstat – Print network connections, routing tables, statistics, etc.
netwatch – monitoring Network Connections.
ngrep – grep applied to the network layer.
nload – display network usage.
nmap – network discovery and security auditing.
nmcli – a command-line tool for controlling NetworkManager and reporting network status.
nmtui – provides a text interface to configure networking by controlling NetworkManager.
nslookup – query Internet name servers interactively.
ping – send icmp echo_request to network hosts.
route – show / manipulate the IP routing table.
slurm – network load monitor.
snort – Network Intrusion Detection and Prevention System.
smokeping – keeps track of your network latency.
socat – establishes two bidirectional byte streams and transfers data between them.
speedometer – Measure and display the rate of data across a network.
speedtest-cli – test internet bandwidth using speedtest.net
ss – utility to investigate sockets.
ssh – secure system administration and file transfers over insecure networks.
tcpdump – command-line packet analyzer.
tcptrack – Displays information about tcp connections on a network interface.
telnet – user interface to the TELNET protocol.
tracepath – very similar function to traceroute.
traceroute – print the route packets trace to network host.
vnStat – network traffic monitor.
websocat – Connection forwarder from/to web sockets to/from usual sockets, in style of socat.
wget – retrieving files using HTTP, HTTPS, FTP and FTPS.
Wireless Tools for Linux – includes iwconfig, iwlist, iwspy, iwpriv and ifrename.
Wireshark – network protocol analyzer.
un site de snippets cli, merci Seb :)
To assign two (or more) commands to a single keybinding, you’ll have to use the following syntax:
<keybind key="A-F4">
<action name="execute">
<command>thunar</command>
</action>
<action name="execute">
<command>osdctl -s 'Thunar'</command>
</action>
</keybind>This will launch the file manager Thunar and prompt osdsh to display the text “Thunar” on my screen.
I believe the command you are looking for is:
sc config servicenamehere start= autoYou'll need to know the name of the service though - to view this from the command line, try this command - this will show all services:
sc query type= service state= allIf you want to see only stopped services, run this command:
sc query type= service state= inactiveThe list of services output by the query can be quite long. You may filter it by using findstr (see post here) . For example
sc query type= service state= all | findstr "ssh"Will select the output lines of the services list that contain the string "ssh"
Note: For some services you may need also administrator privileges, you will notice it on getting the message Access is denied after executing the sc command. In that case open the Command Prompt (Admin) by pressing 'Windows + X' keys.
Raccourcis de base
<Ctrl> + <b> suivi de <c> : Créer un nouveau terminal dans la session tmux active
<Ctrl> + <b> suivi de <n> : Switcher entre les différents terminaux de la session
<Ctrl> + <b> suivi de <X> : Choisir un terminal spécifique (ou X est le numéro du terminal)
<Ctrl> + <b> suivi de <d> : Se détacher de la session tmux (lancer 'tmux a' pour s'y rattacher)
<Ctrl> + <b> suivi de <,> : Permet de renommer un terminal
<Ctrl> + <b> suivi de <w> : Affiche la liste des terminaux disponibles
<Ctrl> + <b> suivi de <t> : Afficher l’heure dans un terminal
<Ctrl> + <b> suivi de <[> : Permet de scroller ligne/ligne (avec les fleches du clavier ou la souris) ou même page/page avec PgnUP et PgnDOWN, tapez "q" pour quiter ce modeCommandes dans un Split
<Ctrl> + <b> suivi de <"> : Split vertical du terminal courant en deux + ouverture d’un terminal dans le nouveau panel
<Ctrl> + <b> suivi de <%> : Split horizontal du terminal courant en deux + ouverture d’un terminal dans le nouveau panel
<Ctrl> + <b> suivi de <o> : Switcher entre les terminaux splittés
<Ctrl> + <b> suivi de <espace> : Changer l’organisation visuelle des terminaux splittés
<Ctrl> + <b> suivi de <Alt> + (flèches directionnelles) : Reduire, agrandir fenêtre du split
<Ctrl> + <b> suivi de <!> : Convertir un split en terminal seul
<Ctrl> + <b> suivi de <q> : Afficher les numéros des terminaux splittés
<Ctrl> + <b> puis saisissez :join : permet de joindre un terminal seul dans un split- Par exemple, après avoir tapé le combo
+ si vous saisissez join -v -s 3.0 -p 50
Où :
-h ou -v : pour horizontalement ou verticalement
-s 3.0 : terminal 3 et volet 0 (volet si écran splitté)
-p 50 : occupation à 50% de la fenêtreIci donc vous ajouterez verticalement, un terminal numéroté 3 et qui prendra 50% de l’espace total.
CQRS Command Query Responsibility Segregation
Une nouvelle façon de concevoir vos applications pour plus de rapidités et une gestion "client" et "fonction"
1) se rendre à l'adresse
http://developer.android.com/sdk/index.html?hl=sk#Other
2) récupérer l'url de la dernière version du SDK pour linux, actuellement:
android-sdk_r24.2-linux
3) faire en ligne de commande sur la machine cible
wget URL_RECUPEREE
( wget http://dl.google.com/android/android-sdk_r24.2-linux.tgz )
4) décompresser l'archive récupérée
tar xf ARCHIVE
( tar xf android-sdk_r24.2-linux.tgz )
5) mettre à jour les sdk déjà présent (attention LONG) accepter les licences :
cd android-sk-linux
tools/android update sdk --no-ui
6) lister les packages pour installer les build tools:
android list sdk --all
7) installer les build tools (prend le numéro de paquet dont le numéro de build tools est le plus grand) accepter les licences
tools/android update sdk -u -a -t "num paquet"
( tools/android update sdk -u -a -t 3 )
VOILA ! dans le répertoire build-tools vous devriez avoir un répertoire du numéro de la version du build-tools qui contient tout les outils pour compiler et décompiler les applications android ;)
( build-tools/22.0.1 )
Fréd.
PS: testé sur un VPS :x
J'aime simplement et pour moi ?
vim
ls
mc
bash (forcement)
xterm
Je sais RSync c'est plus performant mais parfois ftp fait l'affaire ;)
faire des bash en CGI pour générer du HTML ?
"facile" :x
encore faut il activer CGI... :/
Glances, surveillez vos serveurs en ligne de commande
C&C en html5 ! à tester...
merci SebSauvage.
Un super site qui fournit des outils de gestion en ligne de commandes, vraiment sympa, a lire et a étudier
Merci Augustin pour le partage ;)
Un site intéressant ou tout le monde peut partager les lignes de commandes terminal qu'il trouve utiles ;)
Une librairie et des outils en ligne de commande permettant d'avoir une interface a inotify du noyau linux.
inotify permet de voir les evenements interfenant sur le système de fichiers.
pour plus de renseignement :